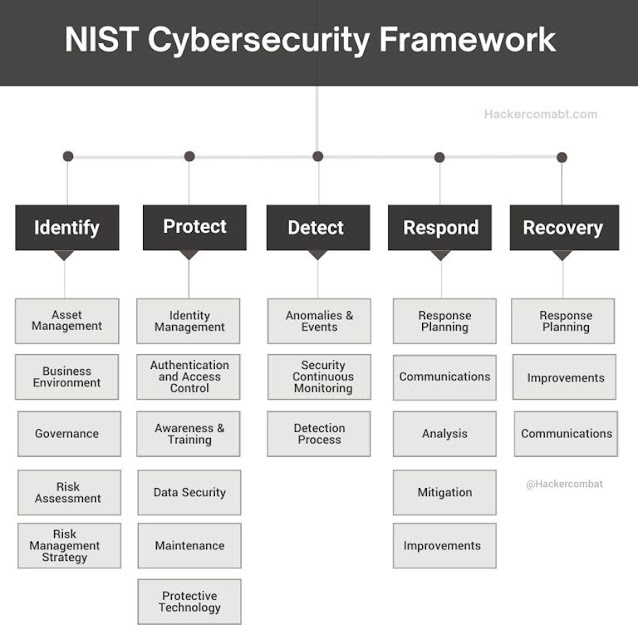
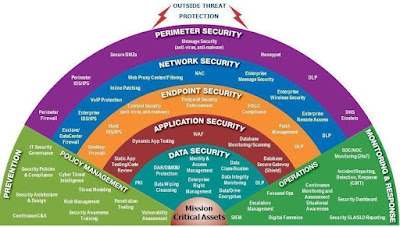
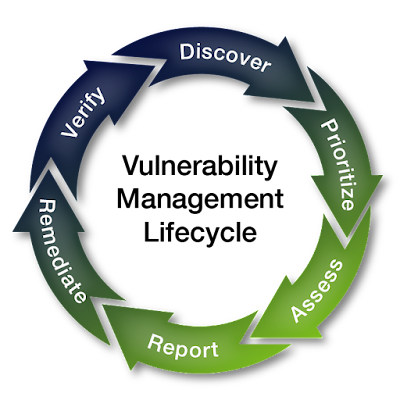
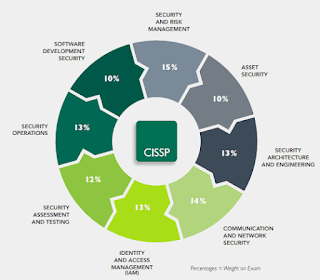
Threat Modelling aims to identify threats and vulnerabilities to apply controls to mitigate the risks. Killing the Cyber Security Kill Chain is an approach for Threat Modelling with ISO 27001 controls. Related to cybersecurity, ISO27001, KillChain, threatmodelling, advanced persistent threat, command and control, cyber security, exfiltration, exploitation, information security, intrusion, isms, iso 27001, kill chain, lateral movement, privilege escalation, reconnaissance, risk management, security controls, threat intelligence. #cybersecurity #ISO27001 #KillChain #threatmodelling #niranjanmeegammana #SLIIT Niranjan Meegammana