Defence in Depth : Load of the Rings in Cyber Security
Image : Michael Fisher
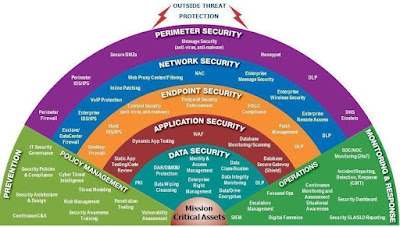
At the heart of your business is data. Protecting your data from malacious actors require using effective strategies. Defense in Depth (DiD) is security strategy that uses series of defensive mechanisms to protect your information assets. Because of layered nature of defences, when a malacious actor breaks one mechanism, the next mechanism steps up to block the attack. DiD is not a new defence concept; the castles of medieval times used ditches, ramparts, draw-bridge, towers, battlements, and gates for defence.
These series of defencive layers can be single or combination of physical, technological and administrative controls.
- Administrative control define organisation policies procedures that restrict certain behaviors to ensure security.
- Technical controls are implemented using software and hardware to protect system resources.
- Physical controls protect systems restricting unauthorized access.
In web applications Defence in Depth achieved with Web Application Firewall (WAF) , session cookies, and application logic.
Following are some considerations for DiD.
- The principle of least privilege ensures all users to have only the minimum permissions to perform their functions, and no more.
- Authentication controls such as password policies, multi-factor authentication
- Network security controls such as firewalls, ingress and egress rules.
- Physical controls like gates, security checks, CCTV, door locks.
- Insider threats protection with segregation of duties.
- Organisation security policies and procedures.
- User awareness and training.
Physical Security
The outer most defence is physical security, which involve fences, walls, security guards, security cameras, and gates etc. They are useful to disallow unauthorized entry. Physical security sometimes combined with technical controls using biomatrics, swipe cards etc. Physical building security and controlling access to computing hardware within the data center critical to prevent external and internal vandalism.
Perimeter Security
Firewalls help protect organisation networks from large-scale Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. It can help filter malacious incoming traffic as well as insider threats that transfer sensitive data outside. The security perimeter expands to each employee with your BYOD policy which address employees using their own devices for office work.
Computing security
Enabling endpoint protection require keeping systems patched and current, as well as providing secure access to virtual machines. Effective virus and malware solutions for protecting each individual computer in the network is critical as when one computer compromised, the malware can spread across the network. Using end point firewalls and software whitelisting is required to protect data stored in end points,. The security strategies must be in place protect potential equipment theft or loss inhouse , customer locations and when travelling. When you discard computers. hard drives or devices may have undeleted data.
Networking security
Protecting internal network by limiting communication is critical between resources. Network segmenting, internal firewalls, intrusion detection are important strategies in DiD.
You need to consider following:
- Identity and access control security
- Control access to device configurations.
- Single sign-on and multi-factor authentication.
- Audit events.
- Deny by default.
- Inbound and outbound internet access
- Secure connectivity in premises networks.
Application security
Ensure applications are secure and free of vulnerabilities. Store sensitive application secrets in a secure storage medium. Make security a design requirement for all application development. Establish best practices of Secure Software Engineering Life cycle (SSDLC).
Data Security
The inner most layer of defence is the data protection. Store data in a database, on disk inside virtual machines, or on cloud storage. Use a data loss prevention mechanism. Introduce data protection policies and adhere to Data Protection Laws like GDPR.
The defence in Depth aims to strengthen the security posture of the organisation to help ensure confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information assets.
Least privilege principal
Restrict access to information only to individuals who have been granted access explicitly to perform their work only. No more.
Acceptable use policy (AUP)
AUP stipulates constraints and practices that a user must agree, to be allowed to access a corporate network, the internet or other resources.
Encryption
Use encryption and fingerprints using a one-way hashing algorithm, when data transmitted from one end to another. Securely store encryption keys to prevent unauthorized access.
Monitoring
Monitor the network for Denial-of-service attacks. Use threat hunting to locate intruders and Advanced Persistence Threats (APT). Use SEIM solution in SOC operations. Monitoring and prevention security strategies include logging, vulnerability scanning, auditing, and threat hunting.
Security Information and Event management (SIEM)
A SIEM an investigative layer, focused to find malicious behaviors in the system to detect and respond to cyber attacks. It provides a dashboard with advanced analytics to the security team before or during an attack.
Threat intelligence
Threat intelligence is critical for assessment of risks on going basis in a changing threat landscape. It uses various data feeds like CVEs, NVD and MITRE ATT@CK etc., providing up-to-date information about indicators of compromise (IoC), known threat actors, their tactics, techniques and procedures (TTP).
Security Awareness Training
In reality the security begin with people. Therefore, security awareness training resides in the outer most defence layer. Humans are the most vulnerable in cyber security. They cannot be patched. Many attack types go after the end user, where social engineering exploit human weaknesses of greed, fear, helpfulness, ambition and negligence etc. Humans have caused majority of the cyber security incidents. Cyber security Policies, Procedures, and Awareness is critical component in Defence in Depth. The first step of DiD is only established, when you have created policies, implemented security procedures, and trained all employees.
Defence in Depth strategy must follow a holistic approach, whereS ISO 27001 internal standard provides a systematic process to establish an Information Security Management System. ISO 27001 guides an organisation to create Information security policy and objectives, conduct risk assessment, creating risk treatment plan, incident response, monitoring, measurement and obtaining ISO 27001 accreditation following an external audit.
Annex A of ISO 270001 provides 114 security controls covering 14 categories of to use in Defence in Depth approach for information security of your organisation.
The domain include:
- Information Security Policies
- Organization of Information Security
- Human Resource Security
- Asset Management
- Access Control
- Cryptography
- Physical and Environmental Security
- Operations Security
- Communications Security
- System Acquisition, Development, and Maintenance
- Supplier Relationships
- Information Security Incident Management
- Business Continuity Management
- Compliance
Stronger Defence in Depth strategy also requires:
- Auditing the systems, data, applications, processes and users to understand where the vulnerabilities are and how attackers can exploit them.
- Implement behavioral analytics to monitor your system and users to detect incidents and identify anomalous behavior. This enables identifying attackers using compromised credentials and malicious insiders.
- Categories, prioritize and isolate your data to limit access to it by unauthorized persons, as well as to prevent use of data for unauthorized purposes by authorized persons.
- Using multiple firewalls to protect internal networks, endpoints. Monitoring and inspect traffic between your devices. Using firewalls both inside and outside the network allows you to prevent lateral attacks and enables system isolation.
- Implement endpoint protection with endpoint detection and response (EDR) technology to detect incidents real time and to increase response speed.
- Implement an efficient incident response system and axplan to detect incidents fast and respond effectively.
- Conduct risk assessments, penitration
testing regularly and adjust your controls or apply new controls to minimize the risks.
Niranjan Meegammana


Comments
Post a Comment