ISMS and ISO 27001 Questions and Answers
1. What is ISO 27001?
ISO 27001 is a comprehensive information security standard, which provides the requirements for an information security management system (ISMS) for certification. It is a framework of policies and procedures that consists of all technical, physical, and legal controls of an Information Risk Management process.
2. What does ISO 27001 certification signify in terms of risk assessment?
ISO 27001 certification guides organizations to identify, analyze, assess and evaluate the information security risks faced by organization information assests.
3. What is the purpose of ISO 27001?
ISO 27001 purpose is to provide the framework to develop an information security management system to control the risks associated with data and systems to minimize information security risks to ensure Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability of data and systems critical to business continuity.
4. What is meant by ISMS?
The Information Security Management System (ISMS) is a systematic approach for organizations to protect and maintain the information assets, from potential risks by applying of physical, technical, and administrative, security controls.
5. What kind of industries prefer ISO 27001 certification?
Any industry that maintains confidential data can use ISO 27001 certification. It includes:
IT Companies
Telecom Industry
Financial Industry
Government Agencies
Healthcare organizations
6. What is the difference between ISO 27001 and ISO 27002.
ISO 27001 standard provides requirements for certification of organizations for information security compliance. ISO 27002 provides provides guidelines on security controls determined in Annex A of ISO 27001.
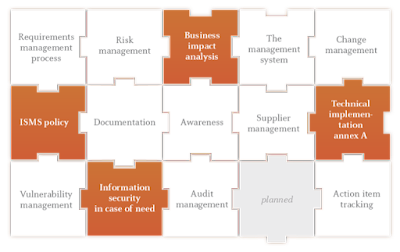
7. What is meant by Annex A of ISO 27001?
ISO 27001 Annex A includes 114 controls, under 14 categories. An organization can choose to implement those controls after a risk assesment.
They cover:
A.5 Information security policies
A.6 Organisation of information security
A.7 Human resource security
A.8 Asset management
A.9 Access control
A.10 Cryptography
A.11 Physical and environmental security
A.12 Operations security
A.13 Communications security
A.14 System acquisition, development, and maintenance
A.15 Supplier relationships
A.16 Information security incident management
A.17 Information security aspects of business continuity management
A.18 Compliance
8. List out the audit controls of ISO 27001.
See above list.
9. What is meant by the CIA triad?
The CIA triad is denoted by Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability, which help
identify the vulnerabilities of an information system.
10. Explain the difference between Symmetric and Asymmetric encryption?
Symmetric encryption uses a shared single key to enable encryption of messages communicated among two parties. It is people used to transfer a large amount of data. Asymmetric encryption uses a pair of keys, which are called public key and private key to encrypt and decrypt the data. It is used to transfer small amount of data.
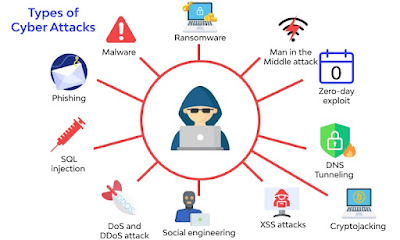
11. Define XSS?
Cross-site scripting is a n attack on web applications. It injects malicious scripts in the target website, which provides message boards, web pages, and forums.
12. What is the difference between Black Hat and White Hat?
Black Hat hackers are the non-ethical hackers who carry out malacious acts for financial benefits. White Hat hackers are the ethical hackers engaged in defensive security to protect the data against Black Hat hackers. They perform penetration testing to strengthen their systems and prevent cybercrimes.
13. Define Regulatory frameworks?
Regulatory frameworks are the set of guidelines and best practices used to achieve the requirements of regulations, strengthen security, achieve business objectives, and enhance security processes.
14. What is an ISO 27001 audit?
The ISO 27001 audit allows the organization to asses compliance of ISMS processes, policies, and controls to the defined requirements ?
15. What are the key objectives of an ISO 27001 audit?
The key objectives of the ISO 27001 audit are:
To find out the issues with the ISMS
To ensure the ISMS is compliant with ISO 27001 standard
To identify the potential improvements to the ISMS
16. List out the types of audits?
Internal audit conducted by internal staff.
External audit conducted by an acredited certification auditor.
17. How often are the external audits performed?
The initial certification audit will be conducted in 2 stages. After that an serveylince audits are conducted every year. A e-certification audit is conducted in the third year.
18. Distinguish between a Lead Auditor and a Lead Implementer
A lead auditor is a professional in the certification body. He leads the audit team to asses organization's ISO 27001 compliance for certification. The Lead Implementer plans, develops, manages and supports the organization ISMS to complying to ISO 27001 standards.
19. What are the steps used for implementing ISO 27001 controls?
Setup an implementation team
Create the implementation plan
Define the ISMS scope, policies and objectives
Define roles and responsibilities
Defines risk assessment methodology
Conduct risk assessment
Establish security baseline and acceptable level of risks
Choose risk treatment options
Develop Statement of Applicability
Create risk treatment plan
Develop ISMS manual
Provide awareness and training to employees, suppliers and vendors
Implement ISMS with chosen controls
Measure, monitor, and review
Implement corrective actions ,
Continuesly improve the ISMS
20. Risk-based approach
Risk-based approach allows organisations to analyze risks involved in business processes, data and systems to identify likelyhood and impact of risks on information assets to prioritize risk treatment to minimize them to an acceptable risk level.
21. What are the basic principles of Information security?
Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability
Authentication, Authorization, Accounting
Quality, Privacy, Trustworthiness
22. Explain Incident Management
Incident Management is a process to prepare, identify, analyse, contain, recover and report information security incidents to ensure business continuity. The incidents are issues such as security breaches, server downtime, malware and cyber attacks.
23. What is the ISO 27001 recommended risk assessment methodology?
The ISO 27001 does not specify a specific risk assessment methodology. It only expect organisation to identify, analyze, and evaluate the risks using a suitable methodology relevant to the information security process of an organization.
24. Define the PDCA method in ISO 27001?
Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) is a four-step approach to define, plan, implement, evaluate and improve the organization ISMS.
25. What are the advantages of ISO 27001 Implementation?
Preventing security breaches
Preventing legal fines and law suits
Preventing loss of reputation
Commercial, contractual, and legal compliance
Retaining customers and achieving new business
Improving strategies and processes
26. Is ISO 27001 certification sufficient to meet GDPR compliance?
GDPR covers the processing and security of personal data. Only ISO 27001 certification is not enough to get compliance with GDPR. The ISO 27701 provides the requirements for complying on personal data protection.
27.Does ISO 27001 impact the emplyees of the organization?
Organizations information security is everyone's responsibility. ISO 27001 certified organizations have to ensure conducting effective staff awareness and training on policies, procedures and security controls relevant to their daily routines.
28. What's the difference between a security flaw and an exploit?
A security fault is a vulnerability in a system or applications that a cyber attacker can exploit to obtain unauthorized access to it or perform unauthorized actions. An exploit is a piece of software, a chunk of data, or a series of commands that exploits a vulnerability to induce unintended or unexpected behavior on computer software, hardware, or electronic devices. Attackers can exploit vulnerabilities to execute code, access a system's memory, install malware, and steal, destroy, or alter data.
29. What is the process for security risk assessment ?
Determine information value to business processes.
Identify and prioritize assets.
Identify potential threats.
Identify vulnerabilities.
Asses the likelihood and impact
Calculate the loss of various scenarios on a per-year basis
Document results in the risk assessment report
30. What is threat modelling
Threat modeling is a systematic approach for identifying and prioritizing potential threats to a system, and determining mitigation measures to reduce or neutralize those threats.
31. Principle of Least Privilege
Ensures that people only have enough access that they need to do their job. This limits the accesss to data to prevent possible data breaches.
32. Principle of Separation of Duties
This principal follows on from the Principle of Least Privilege. The idea is to separate duties in a way that no single role should have too much authority. The person doing sales should not be allowed to approve discounts.
33. Principle of Defense in Depth
Defense in Depth limits access to the system, by establishing layers of security. The defence may involve physical, technical and administrative controls. Technical controls are firewalls, encryption, access control with multi factor authentication, segregation of networks , monitoring etc.
34. Principle of Failing Securely
When an error occurs, the systems should handle it or fail securely without damaging data.
35. Principle of Open Design
The system must be designed with open technologies. For example encryption should use well-designed cryptography implementations that are published publicly.
36. Principle of Avoiding Security by Obscurity
Security must be implemented in design not by obscurity. An example is a username and password should not be hard coded into an application.
37. Principle of Minimizing Attack Surface Area
Remove certain parts used to test an application when it's going into production to make it more secure. Do not have windows in data centers that will allow easy break in.
38. How to Dive Deeper
Have a good threat intelligence system to help build an effective threat model for your organization.
39. Security orchestration
Security orchestration aims to integrate various technologies and security tools, to make them capable of working together and improving incident response.
40. Security Orchestration, Automation and Response (SOAR)
SOAR refers to technologies that enable organizations to collect inputs monitored by the security operations team. SOAR tools allow an organization to define incident analysis and response procedures.
Niranjan Meegammana


Comments
Post a Comment